Option
An option gives the holder of the contract the right to buy/sell an underlying asset for a fixed price at a defined time in the futurue (termed European style options).
- it's a right and not an obligation (much like an insurance)
- execution prior to defined date: American style option
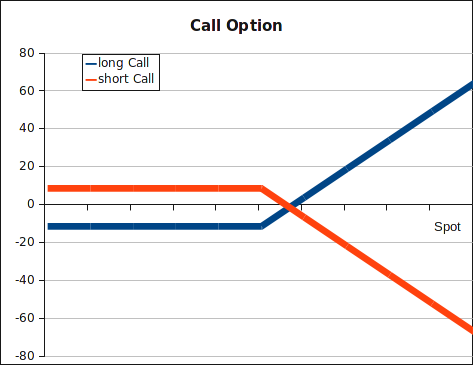
- a call option is the right to buy
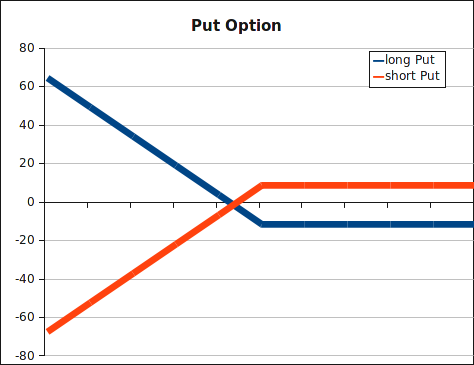
- a put option is the right to sell
The payout of a call option: . (S is stock price at exerc. time, X is pre-defined strike price). A holder of the option will only exercise his right if the price of the underlying asset is above the strike price at time T.
The payout of a put option: . A holder of the option will only exercise his right if the price of the underlying asset is below the strike price at time T.
The premium of an option is usually calculated using the Black-Scholes-Merton formula.
There also exist a number of “exotic” options: …
Payout diagrams: at the maturity of the option, depending on the spot price of the underlying, shown on the x-axis, we will realize a profit or a loss, shown on the y-axis.